 Junior Teacher
Junior Teacher
51. ପିଆଜେଟ୍ ବିଶ୍ଵାସ କରିଥିଲେ ଯେ ଜ୍ଞାନଗତ ବିକାଶ ଏକ ପ୍ରକ୍ରିୟା ମାଧ୍ୟମରେ ଘଟିଥାଏ:-
- A) ସ୍ମରଣ
- B) ଅନୁକରଣ
- C) ସନ୍ତୁଳନ
- D) କଣ୍ଡିସନିଂ
Ans:C) ସନ୍ତୁଳନ
52. In Piaget’s Preoperational stage what does “operation” refer to?
- A) Physical actions and
movements - B) Mental processes and logical
thinking - C) Social interactions with peers
- D) Language development
Ans:B) Mental processes and logical thinking
53. According to Piaget, from which year a child starts to develop self concept?
- A) 11
- B) 13
- C) 14
- D) 12
Ans:D) 12
54. Language is which of the following types of content?
- A) Auditory
- B) Pedantic
- C) Visual
- D) Symbolic
Ans:D) Symbolic
Language is social, arbitrary, symbolic, vocalic, systematic but not instinctive in nature.
55. Which organization oversees the implementation of the Right to Education (RTE) Act in India?
- (A) UNESCO
- (B) UNICEF
- (C) National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)
- (D) World Bank
Ans: (C) National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR)
• UNESCO : United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
• The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) was born on 16 November 1945.
• UNICEF :United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund.
• (UNICEF) was established in 1946, in the aftermath of World War II.
56. In teacher-centric approach of learning teacher act as
- (A) Facilitator
- (B) Guide
- (C) Leader
- (D) None of these
Ans: (C) Leader
57. Which approach of learning says “Spare the road, spril the
child”?
- (A) Teacher centric
- (B) Learner Centric
- (C) Learning Centric
- (D) None of these
Ans: (B) Learner Centric
58. Which approach of learning occupies the vital role in the teaching-learning process?
- (A) Learning-centric
- (B) Learner Centric
- (C) Both
- (D) None of these
Ans: (C) Learner Centric & Learning Centric
59. 3-H co-ordination means co-ordination among
- (A) Hand, head, heart
- (B) Hand, hair, head
- (C) Both A & B
- (D) All of the above
Ans: (A) Hand, head, heart
• 3H = Hand, Head and Heart
• 3R = Reading, Writing and Arithmetic
60. Which of the following is the nature of learner centred approach of learning?
- (A) Based on the
principle of practicability & utility - (B) Based on the principle or variety & elasticity
- (C) based on the need,interest ,ability etc. of learner.
- (D) All of the above
Ans: (D) All of the above
61. Who said, “Education is a bipolar process”.
- (A) Adams
- (B) Frobel
- (C) D.V.
- (D) O.B.Smith
Ans: (A) Adams
62. The first person to describe the learning curve was in 1885.
- (A) Eric Morrison
- (B) Theodore Paulwright
- (C) Hermann Ebinghaus
- (D) Thorndike
Ans: (C) Hermann Ebinghaus
63. କାହା ସହାୟତାରେ ଆମ ରାଜ୍ୟରେ ୧୯୭୫ ମସିହାରେ ପ୍ରାଥମିକ ଶିକ୍ଷା ପାଠ୍ୟକ୍ରମ ନବୀକରଣ ପ୍ରକଳ୍ପ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟକାରୀ ହୋଇଥିଲା ?
- (A) UNICEF
- (B) ଜାତୀୟ ଶିକ୍ଷାନୀତି
- (C) ଜାତୀୟ ପାଠ୍ୟକ୍ରମ ଆଧାର
- (D) ମାଧ୍ୟମିକ ଶିକ୍ଷା ଆୟୋଗ
Ans: (A) UNICEF
UNICEF : The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) was established in 1946,
64. the Tripolar process of education was propagated by
- (A) Chariotte Mason
- (B) Fredrich Froebel
- (C) John Dewey
- (D) Maria Montessori
Ans: (C) John Dewey
65. Discipline based model of curriculum design is basically:
- (A) Learner Centred
- (B) Teacher Centred
- (C) Subject Centred
- (D) Social Reconstruction Centred
Ans: (C) Subject Centred
 The 5E instructional model is based on constructivist learning theory which states that people build knowledge and meaning from their own experiences. It focuses on allowing students to understand the concept over time through a series of established steps or phases. These phases include Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate.
The 5E instructional model is based on constructivist learning theory which states that people build knowledge and meaning from their own experiences. It focuses on allowing students to understand the concept over time through a series of established steps or phases. These phases include Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, and Evaluate.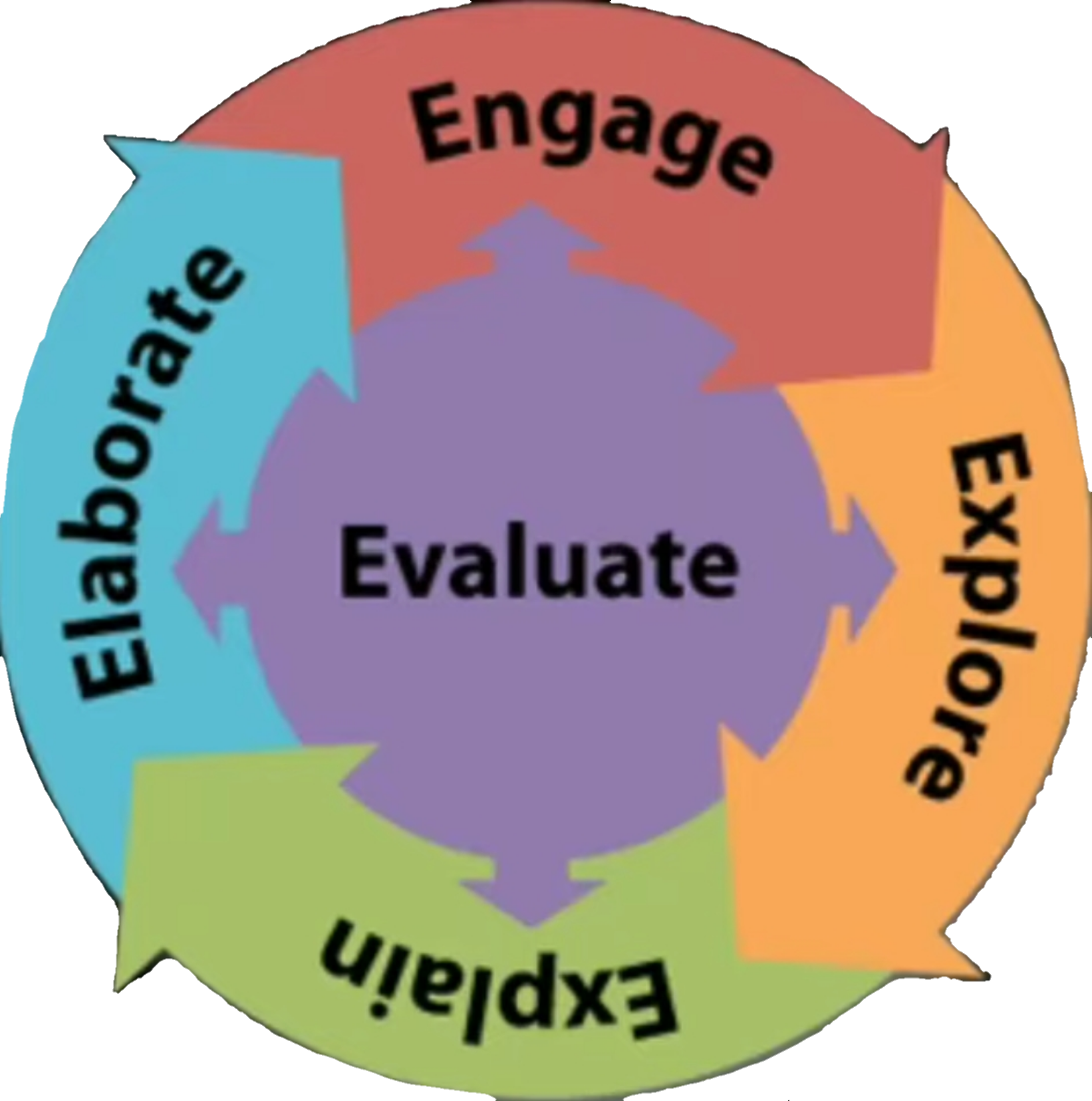 An explanation of each phase step-wise of the 5E model follows:-
An explanation of each phase step-wise of the 5E model follows:-• Engage: Capture the learner’s attention, stimulate their thinking and help them access prior knowledge. For this, the teacher has to create a situation to arouse curiosity among learners.
• Explore: Give time to learners to plan, investigate and collect information and to think and reflect on the data to organize it, to make preliminary meaning. For this, teachers have to facilitate learners with various activities such as group work, discussion, etc.
• Explain: Encourage and involve learners in group work to share and analyze the data they gathered.
• Elaborate: Provide learners with an opportunity to extend and codify their understanding of the concept and/or apply it to a real-world situation. Learners are to be encouraged and guided to apply, interpret, extend and enhance the new concept (scaffolding). Teachers have to facilitate and guide learners in expanding their understanding and developing interpretative /creative abilities as well as reflective and critical thinking.
• Evaluate: Evaluation of learners’ conceptual understanding and ability to use skills begins at the stage of engage and continues throughout the model.
66. The outline of the Contents is;
- (A) Syllabus
- (B) Course
- (C) Programme
- (D) All of these Y
Ans: (A) Syllabus
67. Curriculum is interpreted to mean all the organized courses, activities and experiences which students have under the directions of the school, whether in the classroom or not, is said by:
- (A) John Dewey
- (B) Hilda Taba
- (C) H. Rugg
- (D) Stephen Romine
Ans: (B) Hilda Taba
68. Curriculum reflects the culture of:
- (A) School
- (B) Area
- (C) Home
- (D) Society
Ans: (D) Society
69. Curriculum organization used for different concepts at the same class is:
- (A) Horizontal
- (B) Vertical
- (C) Logical
- (D) None of these
Ans: (A) Horizontal
FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE
• A simile would involve using “like” or “as” to make a direct comparison.
Example:
“Her laughter was like music to his ears.”
• Girish eats like a wolf.
• Compares two different things without using ‘like’ & ‘as’.
• Something is something else.
For example:
Ali is a walking dictionary.
• “The act of giving a human quality or characteristic to something which is not human.”
• Personification would involve giving human qualities to something non- human.
Example: “Her laughter danced in his ears.”
• Hyperbole would involve exaggeration for emphasis.
Example: “Her laughter was a symphony that filled the entire room.”